Abstract
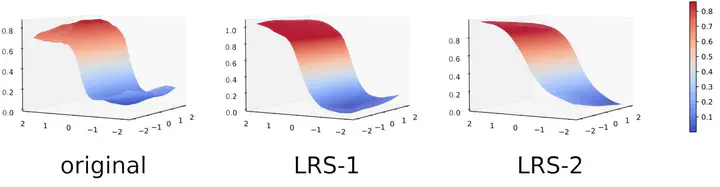
The transferability of adversarial examples is of central importance to transfer-based black-box adversarial attacks. Previous works for generating transferable adversarial examples focus on attacking given pretrained surrogate models while the connections between surrogate models and adversarial trasferability have been overlooked. In this paper, we propose Lipschitz Regularized Surrogate (LRS) for transfer-based black-box attacks, a novel approach that transforms surrogate models towards favorable adversarial transferability. Using such transformed surrogate models, any existing transfer-based black-box attack can run without any change, yet achieving much better performance. Specifically, we impose Lipschitz regularization on the loss landscape of surrogate models to enable a smoother and more controlled optimization process for generating more transferable adversarial examples. In addition, this paper also sheds light on the connection between the inner properties of surrogate models and adversarial transferability, where three factors are identified, smaller local Lipschitz constant, smoother loss landscape, and stronger adversarial robustness. We evaluate our proposed LRS approach by attacking state-of-the-art standard deep neural networks and defense models. The results demonstrate significant improvement on the attack success rates and transferability.